Data security in e-commerce systems
Today's world is an era of digitization and e-commerce. Every day, millions of people around the world make purchases online, entrusting their personal information to various companies and organizations. But how can you be sure that this information is safe? In this article, we will discuss the importance of data security in online stores, the problems associated with breaches of that security, and how technology headless can help secure it.
Table of Contents:
The importance of data security in online stores
E-commerce data security is an integral part of online business and is critical to maintaining customer trust and business prosperity. This provides insight into why investing in digital security, privacy compliance and data protection is not only a necessity, but also a strategic business decision.
First and foremost, consumers using e-commerce services often share sensitive information with online stores, such as personal information, credit card numbers or shipping addresses. If this data gets into the wrong hands, it can be used for identity theft, unauthorized transactions or other forms of cybercrime. Properly securing this data by online stores is therefore crucial to protecting customer privacy and security.
In addition to aspects directly related to customer protection, data security is also important for the online store itself.
Data security breaches can lead to serious financial consequences, such as legal penalties, compensation for affected customers, and costs associated with repairing security systems. It can also damage a store's reputation, resulting in a loss of customer confidence and a drop in sales.
In addition, data security is essential to meet legal requirements. Many jurisdictions around the world, including the European Union with its General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require online stores to implement appropriate data security measures. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in serious penalties.
As a result, data security is not only a matter of ethics, but also a strategic business decision. Proper investment in digital security, privacy and data protection policies, and risk management systems can effectively protect both customers and the store itself from potential threats. Secure online stores earn the trust of customers, which translates into loyalty, long-term relationships and ultimately, business success.
Security and data protection - principles
Data security is an important issue in today's digital world. In particular, online stores that collect and process sensitive customer information must pay special attention to securing this data. Nevertheless, this is not an issue that can be taken lightly - threats to data security, such as hacking attacks, malware, phishing, are increasingly common and can lead to serious consequences.
Forms of hacking attacks
First of all, it's worth understanding the nature of these threats. Hacking attacks can range from a simple attempt to exploit a weak password, to complex techniques like SQL Injection or Cross-Site Scripting, to advanced Man-in-the-Middle attacks. Hackers attempt to gain access to customer data, such as credit card numbers or email addresses, and then use the information for illegal purposes. The most popular of these are:
Malware
Malware, or malicious software, is another major threat. It can be installed on e-commerce servers or customers' computers, usually without their knowledge, to steal data, commit espionage, or launch attacks on other systems.
Phishing
Phishing is a technique that involves impersonating a trusted source, often through fake emails or websites, to trick users out of sensitive information. Even the most informed customers can fall victim to a well-designed phishing campaign.
It is also worth noting that many online stores use less popular solutions or dedicated solutions - proprietary systems or software provided by little-known companies. Such solutions may not have the same advanced security features as professional e-commerce platforms, such as Magento or commercetools, for example. Their security updates may be less frequent or less effective, putting these stores at a disadvantage against potential threats.
Stores using the above solutions must therefore make additional efforts to ensure the security of their customers. This may include regular security audits, implementation of additional layers of security such as two-step authentication, data encryption, or security incident detection and response systems.
Safety education
In addition, an important aspect is to educate both employees and customers of the store on the basics of online security. Employees should be aware of the risks and know how to respond to potential attacks, while customers must not be left without information on how to use the store safely, for example, by regularly changing passwords or checking the authenticity of emails and websites.
The issue of data security in online stores is a complex and constantly evolving challenge. Stores must not only invest in the latest technology and security procedures, but also undertake extensive educational and preventive measures. After all, protecting customer data is not only an ethical and legal issue, but also a key element in building customer trust and loyalty.
What is data leakage and why is it dangerous for a company?
The theft of personal data is an event that can have a wide range of negative consequences for any organization. These consequences include image, legal, financial aspects, and can also affect the level of trust of customers and business partners.
On the image side, data theft can have disastrous consequences. A company that is unable to provide adequate data security can be seen as unreliable or incompetent. This can lead to a loss of trust from both existing and potential customers. In addition, relationships with business partners may be adversely affected, as they may fear the associated risks and decide to terminate cooperation.
Legal and financial consequences of data leakage
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) introduces severe sanctions for data protection violations. For example, the Data Protection Authority (DPA) can impose a fine of up to €20,000,000, or 4% of the total annual worldwide turnover of the previous fiscal year.
These financial penalties can place a significant burden on a company, especially for smaller companies for which such a penalty would cut off financial capacity significantly. In addition, the company may also incur additional costs associated with managing the crisis, such as legal costs, PR, or the need to implement new security systems.
Examples of data theft and their consequences
Examples of data theft are not in short supply. Recall, for example, the 2019 scandal, when the data of 50 million Facebook users was used for political purposes. Such incidents show how serious the consequences of a data security breach can be.
Examples of stores that have fallen victim to attacks that lead to leaks of customer data:
digital.co.uk - leaked data such as email addresses and password hash
neo24.pl - leaked customer database that led to sending out an SMS campaign leading to a phishing site for payments.
morele.net - In 2018, data such as name, email address, password hash and phone number were leaked. Initially, the UODO fined the morele.net store €660,000, but the fine was overturned in court.
Aleleki.pl - leaked data such as name of the entity, address of the entity, VAT ID of the entity, REGON of the entity, PESEL, name of the contact persons, phone number, e-mail address and information on transactions.
RODO, UODO and Polish law
In Poland, data security is regulated by RODO, UODO and other laws. These laws are designed to protect personal data and oblige organizations to ensure an adequate level of security. Violations of these regulations can result in serious legal and financial consequences.
What steps must your company take if a security breach is discovered that may have led to a data leak or the company has lost access to accounts that have access to personal data?
informing the President of the Office for Personal Data Protection by email or postal mail,
Conduct a security audit to investigate the source and cause of personal data leaks
Informing customers about the leak of their data
Taking security measures and preventing further leaks (e.g., resetting user passwords)
Native Magento vs Headless - differences in the big picture
Understanding the differences between native Magento and the headless approach, where Magento is used as a backend and the frontend is a separate application, is crucial for online stores. The choice between the two approaches depends on many factors, such as the needs of the store, available resources and business goals.
Security is one of the most important factors to consider. In native Magento, many security features are built directly into the platform. These include protection against XSS attacks, SQL Injection, password security and HTTPS support.
Security - Advantages of native Magento solutions
Open community
Being one of the most popular e-commerce solutions on the market, it has a huge community of developers and users. This ensures that any security vulnerabilities are quickly identified and fixed. The community regularly shares security tips and practices, which can effectively help ensure the protection of the store. These vulnerabilities do not only affect the backend layer (which Headless uses) but also the frontend layer, so the level of security at both is high. Magento regularly releases security patches. This means that the software developer actively monitors and responds to potential threats, providing stores with tools to defend themselves against new types of attacks.
Advanced security features
Another good feature is advanced security features. Store owners have access to tools and configurations that allow them to customize the security level of their store according to their individual needs.
Audits and inspections
Due to the open nature of Magento, store owners and their technical teams can conduct thorough source code audits to identify and fix potential vulnerabilities. Many companies specialize in Magento security audits, providing expertise in securing this platform.
Security - Disadvantages of native Magento solutions.
Exposing the backend
In native Magento, the user interface and backend are tightly coupled. This means that end users have direct access to the Magento application, which can increase the risk of attacks.
Vulnerability to DDoS attacks
Magento, like any e-commerce platform, can be vulnerable to DDoS attacks, which can be particularly damaging to online stores, leading to downtime and lost sales.
Complexity of the system
Magento is a powerful system, but its complex architecture can create additional points of vulnerability. For example, each extension or module that is added to the system can potentially introduce new security vulnerabilities. The larger the attack surface ("attack surface"), the greater the risk.
The need for regular updates
Magento regularly releases security patches and updates that must be installed to ensure optimal security. Unfortunately, many stores neglect these updates, which can lead to serious security problems.
Weak default security features
Although Magento offers many advanced security features, some of the default settings may not be strong enough. Online stores need to actively work on securing their platform, which may require additional resources and technical expertise.
Security in headless technology
Headless technology is a modern approach to e-commerce, which involves separating the presentation layer (frontend) from the business logic layer (backend). This solution allows for greater flexibility and security, as well as better integration with other technologies.
You can read about why you should invest in Headless store technology in our blog article:
Among the most important safety features of Headless technology are:
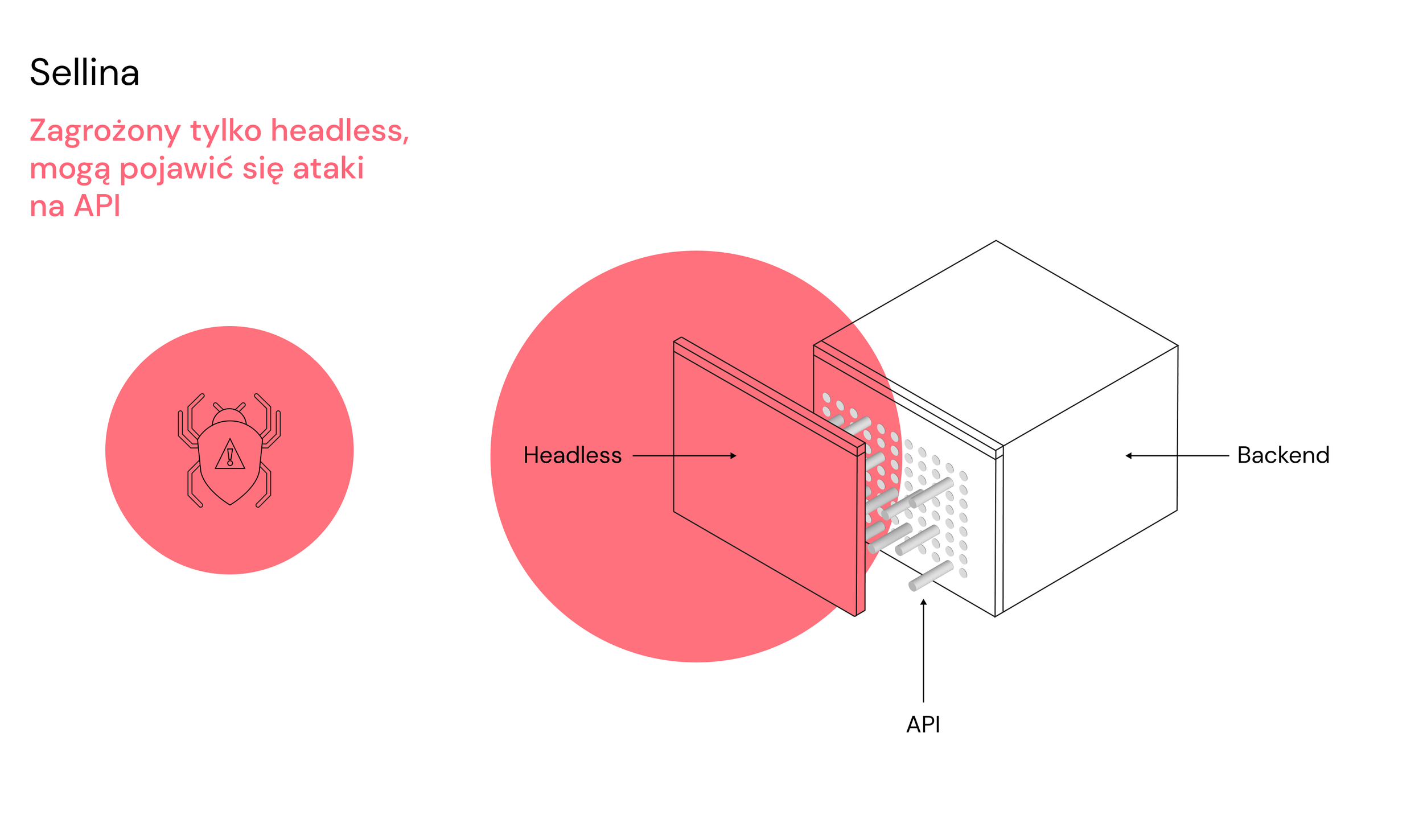
Separation of the frontend and back-end layers
In the headless model, the frontend (user interface) is separated from the backend (Magento). Thus, the end user does not have direct access to the store's backend, reducing the risk of potential attacks.
Reducing the attack surface
By separating the frontend from the backend, the attack surface is greatly reduced. Attacks can only target specific API endpoints, which are carefully secured and monitored.
Flexibility in the choice of frontend technology
Online stores based on the headless model have more freedom in choosing frontend technology. They can choose the technology that offers the best security and is best suited to their specific needs.
Easier management of updates and security patches
Because the frontend is separated from the backend, e-commerce stores can more easily manage updates and security patches. Updates can be deployed independently at each layer, minimizing the risk of introducing bugs or security vulnerabilities.
Scalability and performance
Headless architecture is more scalable and efficient, which can help protect against DDoS attacks. Since the load is spread between the frontend and backend, the store is less susceptible to overload.
Data security
By separating the frontend from the backend, customer data is better protected. Sensitive data is stored only in the backend, reducing the risk of data loss or theft.
How can our Sellin technology strengthen company and customer data security?
In addition to the standard solutions that come with Headless itself, our Sellina solution stands out:
The end user never has direct access to the admin and to Magento. Magento in our solution is hidden "for the world" and there is no way to get into the admin panel in an unauthorized way, for example,
Magento is completely decoupled from the frontend layer by introducing a dedicated API that serves as a proxy between the frontend and backend layers. All requests that want to fetch resources from Magento are translated and filtered through the API which then connects to Magento in its own way,
The frontend layer uses the backend layer only when necessary. Searching the product catalog or blog by users does not use Magento resources. Product information is indexed properly in a separate database (ElasticSearch) and this API directly connects to it,
The front-end application is written in NEXT, in which part of the code (the more sensitive one) is executed on the server and the rest on users' devices.
Summary
Data security in online stores is extremely important, both from the point of view of customers and the stores themselves. A potential data leak could mean hefty financial penalties for the company that was responsible for its administration.
Native solutions are high-level systems, which can make them more difficult to secure. In addition, the combination of frontend and backend means that unauthorized access to data, can be easier than with alternative solutions.
Headless technology offers new, more effective methods of securing data. By separating the frontend and backend, which are connected to each other via APIs, online stores can provide their customers with maximum security.
Do you have an idea, a ready-made specification, or a business need?
Make an appointment for a free consultation.